

With increase in the construction activities in the last two decades, particularly in the building and infrastructure sector, it has been observed that many structures are already showing signs of distress. Thus, repair and rehabilitation of concrete structure becomes necessary to extend its life to ensure the durability of the structure.
Post installed rebaring is one very common technique to increase the strength of the structure by means of jacketing. It is also used for addition or alteration of existing structures to suit the current purpose. Many a time, the more conventional way of dismantling and replacement of the existing portion of the structure and welding the new reinforcement to the existing one is preferred to the post installed rebaring concept. However, this idea is detrimental to the structure in the perspective of sustainability of the structure.

Advantage of post installed rebaring:
Post installed rebaring is simply adding reinforcement to an existing concrete structure such that the structure behaves as a cast in reinforcement.
Main advantage of this type of connection are as follows:
- Design flexibility
- Form work simplification
- Reliable like cast in
- Defined load characteristics
- Horizontal, vertical and overhead applications
The main principle of using post installed reinforcement connections is how the load is transferred in reinforced concrete. The transfer of load or stress is based on the bond between the reinforcing steel and the surrounding concrete.
Since chemically bonded rebars result in failure of concrete, adhesive-concrete interface or anchored reinforcement bar, the ultimate resistance can be predicted through the sum of the contribution of concrete strength, properties of adhesive used and anchorage depth.
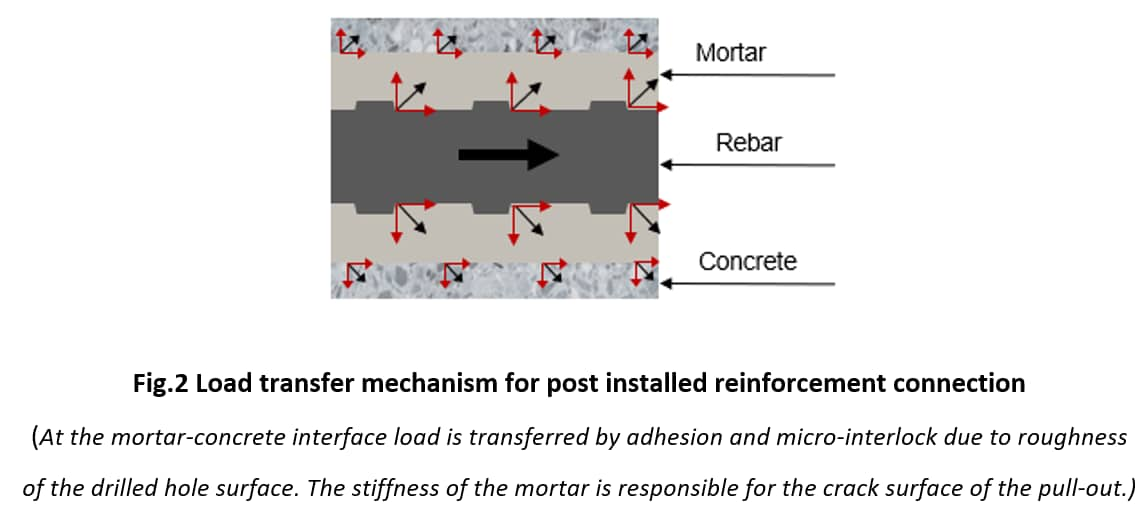
Post-installed rebars become part of the structural system and must be designed as carefully as the entire structure. While European Technical Approvals prove that in basic load situations, post-installed rebars behave like cast-in bars, number of differences needs to be considered in special design situations such as fire or load cases where hooks or bends would be required for cast-in anchorages. The task of structural rebars is to take tensile loads and since concrete failure is always brittle, reinforced concrete design assumes that concrete has no tensile strength. Therefore, structural rebars can end / be anchored in only two situations:
- The bar is not needed anymore (the anchorage is a node in equilibrium without tensile stress in concrete)
- Another bar takes over the tensile load (overlap splice).
Testing and assessment of post installed rebar:
Testing and assessment of post installed reinforcement connection is important for the following reasons:
1. Performance evaluation of the system
2. Based on this assessment document, testing laboratories issue product certification to individual manufacturers for the respective products
3. Technical approval of every product is essential for ensuring a safe post-installed rebaring system
4. The technical approval consists of the manufacturer’s installation instructions (e.g. drilling technology, hole cleaning etc.)
EOTA EAD 330087-00-0601 is the assessment document for systems for post installed rebar connections with mortar. The qualification test program includes considering the following:
1. Service condition tests
a) Bond resistance of post installed adhesive system
b) Bond/ splitting behavior of post installed adhesive system at deep embedment depth
2. Reliability tests
a) Sensitivity to hole cleaning
b) Sensitivity to free/thaw conditions
c) Sensitivity to sustained load
d) Decreased installation temperature
e) Sensitivity to installation direction
3. Injection verification
4. Chemical and corrosion resistance
Design calculation:
Design of post-installed reinforcing bar connections requires that the type, size, spacing and quantity be established for the connection. This is typically based on either direct calculation of section forces or a requirement to match existing reinforcement. Density and sizing of dowels for shear transfer between new overlays on existing structural elements such as slabs and walls may be based on other considerations. Additional design considerations may include:
- loading type (sustained, seismic, shock)
- fire requirements
- corrosion resistance
- detailing requirements based on element type (integrity reinforcement, etc.)
The design of post installed rebar connection is done as per the guidelines of EN 1992.1.1-2004 “Design of concrete structures” and EOTA TR 023 “Assessment of post installed rebar connections”.
The basic anchorage depth is calculated as follows:-

Where, ssd is the stress in the bar at the position from where the anchorage is measured from and fbd is the design value of ultimate bond stress for ribbed bars.
The design anchorage length is calculated as follows:-

Conclusion:
A design concept taking explicitly into account splitting of concrete and bond of reinforcement has been derived from the provisions of EOTA TR023. Anchorage designed according to this concept has the great advantage of clearly showing the possible failure modes and the achieved safety level. Moreover, it is possible to differentiate between bars with a specific bond strength, which depends on the rib geometry for cast-in, and on the bonding agent for post-installed bars. The analysis of a large number of tests has shown that the proposed concept is applicable to both cast-in and post-installed bars. Since the behavior of anchorages and splices with post-installed reinforcement therefore on the characteristics of the bonding agent, it is advisable that only products, which have been qualified by specific tests be used with the proposed method.
The rebar anchorage can be calculated with Hilti injection systems according to the most-updated state-of-the-art design codes and Hilti methods.
In case you need more support to understand which qualification is most suited to your application requirement, please leave a comment on this article or post your question in our Q&A section.
For further information, please contact a Hilti Field Engineer or write to us at:
TeamEngineeringSupport.IN@hilti.com

